Transformers are among the most critical assets in today’s power generation and transmission systems. Not only design and upkeep, but also the quality of transformer oil, decides their reliability. Transformer oil gets exposed to oxidation, moisture, and thermal stress over time, resulting in performance deterioration and ultimate transformer breakdown. To overcome these challenges, transformer oil regeneration has become a proven and reliable technique for restoring aged oil to a like-new condition, reducing costs, and extending transformer life.
As a manufacturer with decades of experience in developing and producing transformer oil regeneration machines, we have witnessed the way that high-tech regeneration can help power plants, substations, and industrial consumers achieve both operational reliability and environmental sustainability. Here in this article, we will talk about the role of transformer oil, why it ages, and how the transformer oil regeneration principle and equipment work in practice.
The Role of Transformer Oil in Power Plants
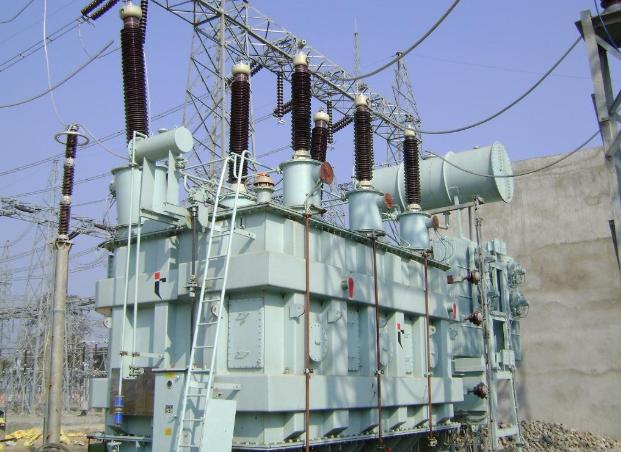

Transformer oil is not just a liquid filling in a transformer — it is an all-purpose medium that ensures stable and secure operation of power equipment. In power plants, where transformers are typically loaded and operating in altered conditions, the oil serves three critical functions:
- Dielectric Insulation: Transformer oil damps electrical discharges by functioning as insulation among energized components, reducing the chances of breakdowns.
- Heat Management: Through circulation within the transformer, oil readily absorbs heat from windings and cores, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Protection Against Contaminants: The oil acts as a protective film that minimizes contact between internal parts and external contaminants such as oxygen and moisture.
Without adequately serviced transformer oil, even the most robustly built transformer would face increased opportunities for partial discharge, overheating, and premature failure. It is because of this that oil quality maintenance is just as vital as keeping the mechanical integrity of the transformer intact.
Causes of Transformer Oil Aging
Even under optimal operating conditions, transformer oil is constantly being subjected to physical, chemical, and electrical stresses. With age of service, these stress factors will gradually alter their composition and operation. The major causes of oil aging are:
- Thermal Stress Over Time – High operating temperature accelerates the breakdown of hydrocarbons in the oil at the molecular level, forming by-products that reduce its insulating strength.
- Catalytic Action of Metal Surfaces – Exposure to copper, iron, and other metals in the transformer may drive oxidation reactions faster, especially if oil flow is low.
- Entry of Foreign Contaminants – Tiny leakage by gaskets or poor sealing systems offers a pathway to air and water entry, stimulating the production of acid and reducing the dielectric strength.
- Accumulated Oxidation By-Products – Sludge and acids formed during the oil gradually build up on windings and cooling passages, slowing the dissipation of heat and encouraging hot spots.
- Electrical Stress Events – Voltage surges or partial discharges may initiate localized degradation of oil molecules, generating gases and encouraging the aging cycle.
The cumulative effect of these conditions is a progressive decrease in oil performance, which, if neglected, decreases transformer life and the likelihood of costly failures.
How to Decelerate Transformer Oil Degradation?

While natural ageing of transformer oil cannot be avoided, its pace can be significantly slowed by following good operating practices and precautionary measures. In our experience of working with power plants and utilities, the following techniques are found to be very effective:
- Adopt Condition-Based Monitoring: Regular monitoring of parameters such as breakdown voltage, interfacial tension, and acid number allows early indications of oil degradation to be detected well before any significant damage occurs.
- Operate Under Controlled Environment: Maintaining transformers within loading capacities and making sure cooling systems function properly reduces thermal stress on the oil.
- Improve Sealing and Breather Systems: New sealing techniques and quality silica gel breathers reduce moisture and oxygen ingress, both of which encourage chemical aging.
- Apply On-Site Oil Treatment or Regeneration: Instead of permitting oil properties to fall below acceptable values, routine use of a transformer oil regeneration machine restores valuable qualities, prevents sludge formation, and extends service intervals.
- Training and Maintenance Discipline: Operators trained in best practices of transformer operation can prevent incidental contamination and maintain oil in ideal condition.
By adopting these measures collectively, not only do operators decelerate oil degradation, but they also guarantee long-term transformer reliability and reduce overall maintenance costs.
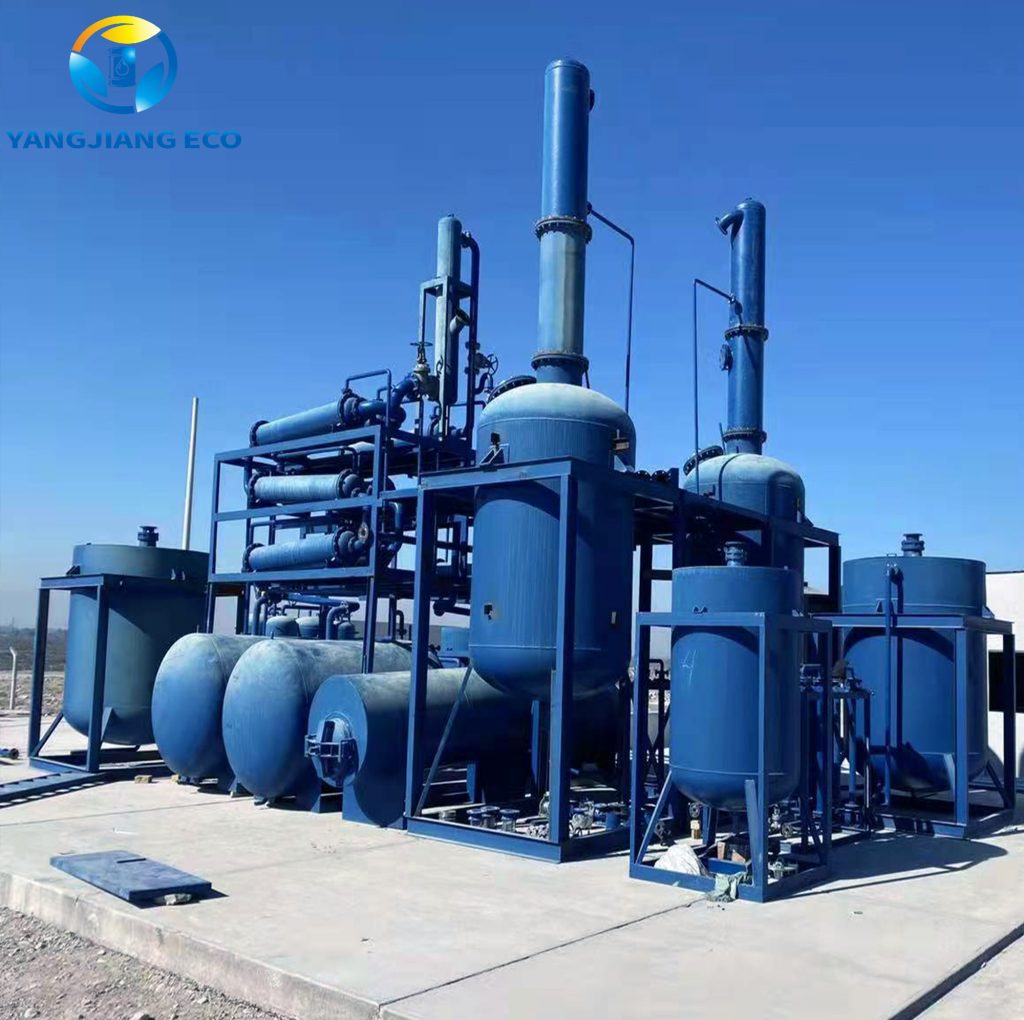
General Transformer Oil Regeneration Principles
Transformer oil regeneration is founded on the concept of rebalancing the chemical and physical properties of aged oil to those of equivalent fresh oil. While filtration or dehydration are straightforward processes that only remove free water and solid impurities, regeneration is a complete processing operation with the intention of removing the causes of oil degradation.
The core philosophy is the removal and elimination of aging by-products, such as acids, sludge, and oxidation residue, that accumulate in the oil over time. Purification and adsorption technology are used to extract these impurities from the oil, while the required insulating properties are reinstated.

Another essential principle is restorative sustainability. Instead of wasting exhausted oil and replacing it with costly new supplies, regeneration extends the productive life of existing oil. Besides lowering the costs of operation, this saves the environment from being wasted by minimizing waste and reducing pressure on new oil production.
We have seen from our experience how proper use of regeneration can make transformer oil recyclable and reusable numerous times during the lifecycle of a transformer, while maintaining reliability, reducing utility and power plant operators’ total cost of ownership.
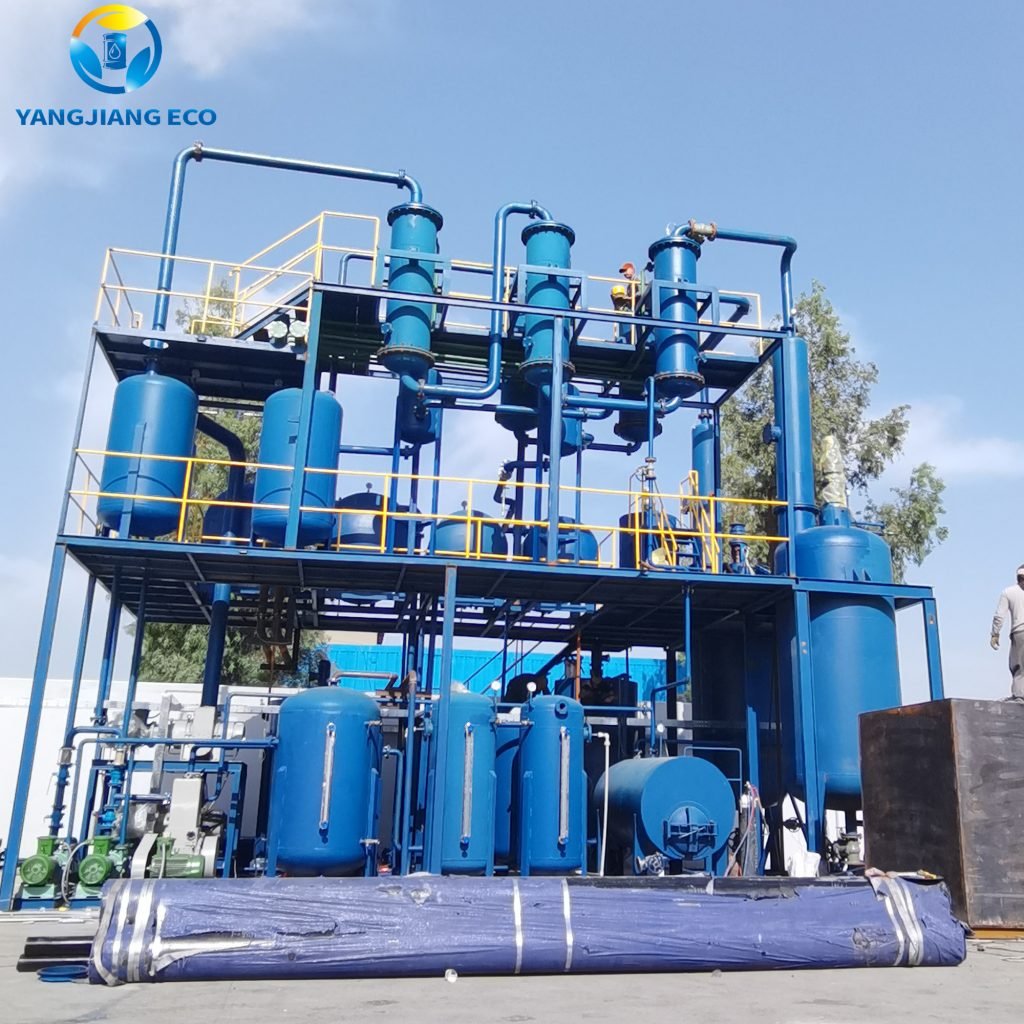
What is the Transformer Oil Regeneration Process?
The transformer oil regeneration process is a systematic sequence of treatments to restore aged oil to a quality comparable to international standards. Unlike simple purification of oil, which focuses mostly on the elimination of particles and water, regeneration is intended to eliminate chemical degradation products and restore the original dielectric and thermal properties of the oil.
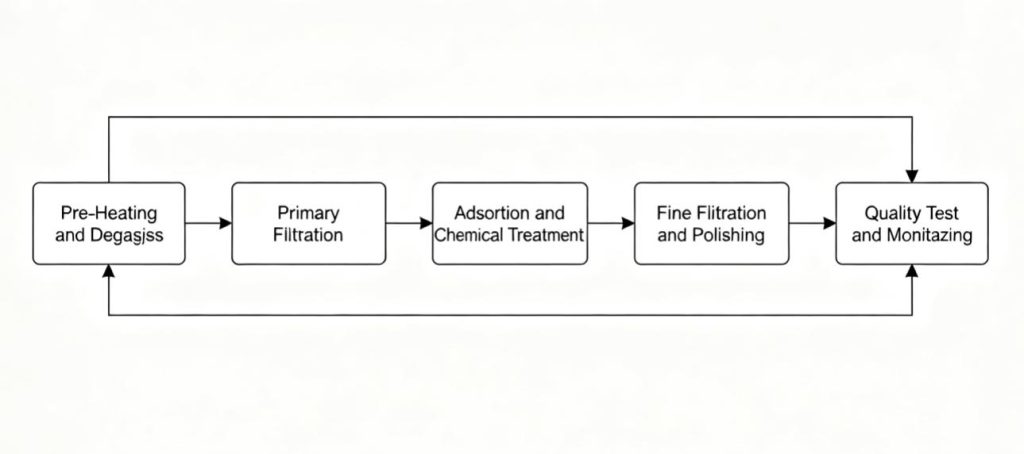
One popular regeneration process includes the following steps:
- Pre-Heating and Degassing – The oil is preheated gently and passed through a vacuum system that removes dissolved gases and entrained moisture, the primary reasons for dielectric failure.
- Primary Filtration – Suspended solids, sludge particles, and other physical impurities that are picked up during transformer operation are caught by mechanical filters.
- Adsorption and Chemical Treatment – There is an application of specialized adsorbent media for the removal of acids, oxidation residues, and other soluble impurities, not removable by mere filtration. This process is of utmost importance because it restores the chemical stability to the oil.
- Fine Filtration and Polishing – Following chemical restoration, the oil is subjected to polishing filtration to offer transparency and high dielectric strength.
- Quality Test and Monitoring – Each batch of regenerated oil is tested for critical parameters such as breakdown voltage, water content, acidity, and interfacial tension to make sure they pass IEC and ASTM standards.
With the multi-stage process, transformer oil is able to be reused and re-regenerated multiple times, giving operators a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option to continuous oil replacement.
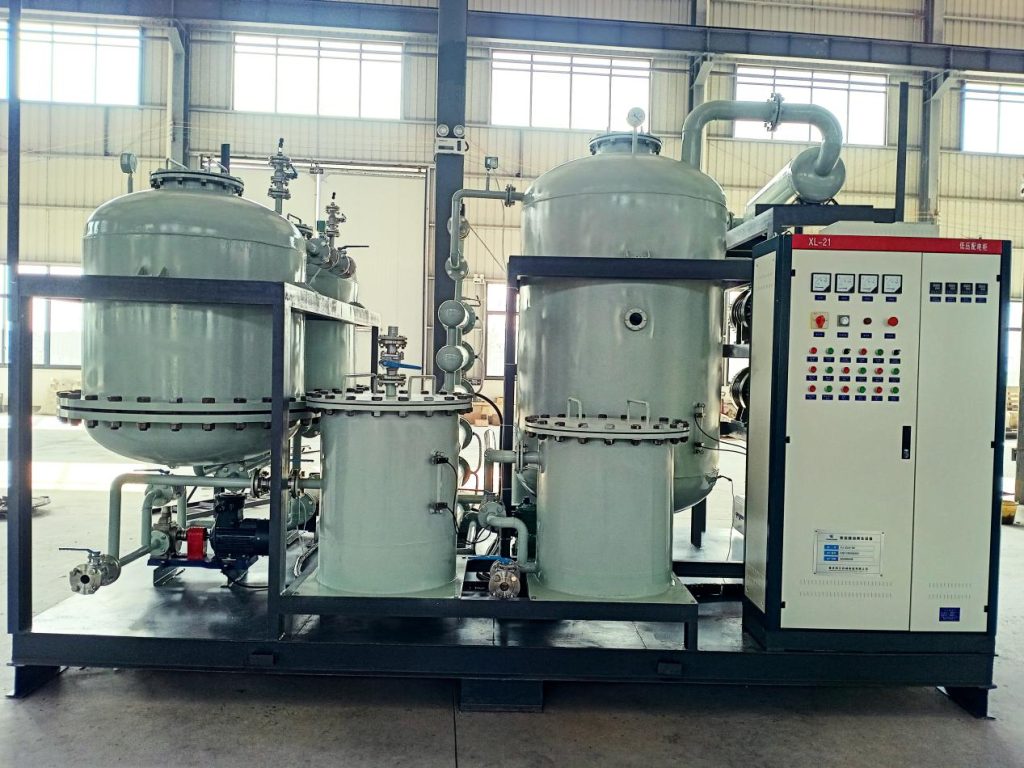
Why Use a Transformer Oil Regeneration Machine?
For utilities and power plant operators, the reliability of transformers is not only a technical imperative but also an economic one. A transformer oil regeneration machine presents a cost-effective and environmentally sound way of refurbishing old oil in situ directly, without the cost of new oil replacement or extended downtime.

Unlike conventional purification units, regeneration machines have several advantages:
- Extensive Restoration – Instead of draining only water and solid impurities, the equipment extracts acids, sludge, and oxidation by-products, bringing the oil to the level of insulating and chemical stability.
- Economic Efficiency – By extending the life of a specific oil, operators reduce the need for new oil buys and eradicate costly oil disposal.
- Prolonged Life of Transformer – Clean and chemically stable oil reduces thermal stress and protects windings, prolonging the life of power assets by a significant extent.
- Green Policy – Regeneration encourages recycling and reduces the environmental impact of oil waste, aligning with the objectives of modern sustainability.
- Operation Flexibility – Our transformer oil regeneration plant is adaptable to online and off-line operations, allowing operators to perform maintenance without disrupting the power supply.
Based on our position as an experienced transformer oil regeneration machine manufacturer, a sound regeneration system investment is not just about maintaining oil quality—it is about transformer protection, lowering operation costs, and creating long-term stability for the power grid.
If you business are considering invest in transformer oil regeneration machines, please feel free to contact us!
Recommended Products





